Create Wizard-Based Order Processing Module in Oracle Application Express
Part II of IV
Section 6.10 – Page 12
|
After selecting an existing customer or
creating a new one, the next step in the Order Wizard is to add items to the
order. In this section, you learn many techniques about how to display
products and add them to the cart like the ones available on the web.
Section 6.10.1 – On this page the following tasks are performed:
a.
Page template set similar to Page 18.
b.
Added a function productPopup in JavaScript section to
display product details in a popup window. This technique demonstrates how a
page is displayed within a web page in Oracle APEX.
c.
Added Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) in HTML header section to
position and style page elements. Check out this blog post which shows How to Use CSS in Oracle APEX.
Section 6.10.2 – In this section a
PL/SQL Dynamic Content region is created to display the following
information:
a.
Customer information: This region displays name and other
details of the selected customer.
b.
Products: Displays all products from the products table.
c.
Current order: This area hold items selected in the current
order along with price, quantity, and totals.
Section 6.10.3 – Create a List
region named Order Progress to hold Order Wizard list similar to 6.6.3 and
6.8.4.
Section 6.10.4 – Create three
buttons CANCEL, PLACE ORDER and PREVIOUS. For the Place Order button, select
a condition type Exists (SQL query returns at least one row) and type select
1 from apex_collections where collection_name = 'ORDER'. This condition
ensures that the current order has at least one item selected to proceed
further. Also note that the button Place Order becomes visible only after
adding a product to the Current Order pane. See Display Current Order in the post “Using HTML in PL/SQL” for details on APEX_COLLECTION.
Section 6.10.5 – This section
demonstrates the use of hidden items in Oracle APEX. The first hidden item,
P12_PRODUCT_ID, is created and used in subsequent sections to Add/Remove
members from Apex_Collections. The other one, P12_CUSTOMER_NAME, is used in
the following computation section. You also set the attribute Value
Protected to No. Specifying Yes will prevent the hidden
value from being manipulated when the page is posted.
Section 6.10.6 – A computation
section is created under Page Rendering to display complete customer name. It
is merely added to the application to show the use of computation in Oracle
APEX. The actual customer profile is displayed on the page using PL/SQL code Display
Customer Information under section 6.10.2 in conjunction with CSS.
Section 6.10.7 – This section
comprises two PL/SQL processes Add product to the order collection and
Remove product from the order collection based on P12_PRODUCT_ID
defined in section 6.10.5. The referenced collection name ORDER was created
in Page 11 - section 6.6.7. Condition Types are set to ADD and REMOVE
respectively. These two expressions refer to the ADD and REMOVE requests sent
through the <a> tag in Display Products PL/SQL block under
section 6.10.2 (see page 113/114 in the book). After receiving the request, the
appropriate process is run to ADD/REMOVE product to/from the Current Order
section.
Section 6.10.8 – Place Order is the
final process in this page that is invoked when Place Order button is
pressed. This PL/SQL block writes data to relevant database tables using page
items and Order collection. The collection ORDER is truncated after the data is
inserted using the statement: apex_collection.truncate_collection(p_collection_name => 'ORDER');
Section 6.10.9 – Create two branches
in this page one each for Place Order and Cancel buttons. When
the Place Order button is clicked, the wizard switches forward to Order
Summary page (Page 14) and moves back to Order Master page (Page 4) when
the Cancel button is pressed.
|
Section 6.12 – Page 20
|
In order to provide product details to the user before placing
orders, you create a popup page that open within the existing order page to
display product's image, description, category, and price. A popup window
doesn’t need to have either a breadcrumb or a tab associated to it;
therefore, none of these options were selected during the page creation
wizard.
Section 6.12.1 – Modify attribute of the newly created page and set template to Popup to open it in an existing one.
Section 6.12.2 – Create a SQL Report
region to hold product image. Using a SQL statement fetch the image of the
selected product based on P20_PRODUCT_ID (a hidden page item created in
section 6.12.5). Following is the SQL statement and explanation of the few
Oracle expressions used in it:
select
decode(nvl(dbms_lob.getlength(product_image),0),0,null,'<img
src="'||apex_util.get_blob_file_src('P6_PRODUCT_IMAGE',product_id)||'"
/>') image
from demo_product_info
where product_id = :P20_PRODUCT_ID
DECODE Function: In Oracle/PLSQL, the
decode function has the functionality of an IF-THEN-ELSE statement. It
compares expression to each search value one by one. If the exprssion is equal to a search,
then Oracle Database returns the corresponding result. If no match is found,
then Oracle returns default. If default is omitted, then Oracle returns null.
In the above statement, the Decode function assesses if the returned value of
product image is zero, store null to the result. The following syntax
and example of the Decode function elaborates it further.
Decode Syntax:
decode( expression , search , result [, search , result]... [,
default] )
Example of Decode Function:
Select customer_name,
decode(customer_id,1,'A',2,'B',3,'C','D') result
From customers;
The IF-THEN-ELSE statement for the above Decode function would
be:
IF customer_id = 1
THEN
result := 'A';
ELSIF customer_id = 2
THEN
result := 'B';
ELSIF customer_id = 3
THEN
result := 'C';
ELSE
result := 'D';
END IF;
NVL Function:
In Oracle/PLSQL, the NVL function lets you substitute a value
when a null value is encountered. The syntax for the NVL function is:
NVL( string1, replace_with )
Example of NVL Function:
Select NVL(customer_state, 'N/A') from customers;
The NVL function in the above statement evaluates that if the
customer_state column is not null return the value it contains. Otherwise,
return the ‘N/A’ string.
DBMS_LOB Package: LOBs, or Large
OBjects, are Oracle's preferred way of handling and storing non-character
data, such as mp3s, videos, pictures, etc., and long character data. Binary
large objects, or BLOBs, and character large objects, or CLOBs, can store up
to terabytes of data - much more than the paltry 4000 bytes permitted in a
varchar2 column.
GETLENGTH(): It is a PL/SQL
Functions of the DBMS_LOB package to read or examine internal and external
LOB values and get the length of the LOB value. Type the following SQL
statement in SQL Plus or another utility:
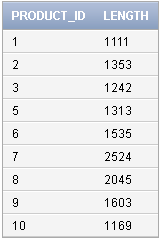
Select product_id, dbms_lob.getlength(product_image) Length from
demo_product_info order by product_id;
Output of DBMS_LOB.GETLENGTH Function:
IMG and SRC: In HTML, images are
defined with the <img> tag. The <img> tag has no closing tag. To
display an image on a page, you need to use the src attribute. Src stands for
"source". The value of the src attribute is the URL of the image
you want to display.
Syntax for defining an image:
<img src="url" alt="some_text"/>
The URL points to the location where the image is stored.
APEX_UTIL.GET_BLOG_FILE_SRC: See section 6.4.2 in Part IV of this blog post.
Section 6.12.3 – Create another SQL
Report region to display product’s text information (name, description,
category, and list price).
Section 6.12.4 – Create a button in
the popup page to allow user to close it. The javascript:window.close()
method is used to give a close link in the popup you created. The close
method closes only windows opened by JavaScript.
Section 6.12.5 – Create a hidden
item named P20_PRODUCT_ID to act as a parameter for the SQL queries mentioned
in the preceding sections.
|